


Next: Efficient mapping of
Up: Scientific Results
Previous: A Direct Image
J. Martin--Pintado , R. Neri
, R. Neri ,
C. Thum
,
C. Thum , P. Planesas
, P. Planesas , R. Bachiller
, R. Bachiller
 Centro Astronómico de Yebes (IGN), Apartado 148, E-19080
Guadalajara, Spain
Centro Astronómico de Yebes (IGN), Apartado 148, E-19080
Guadalajara, Spain
 IRAM, 300 rue de la Piscine, F-38406 St Martin d'Hères, France
IRAM, 300 rue de la Piscine, F-38406 St Martin d'Hères, France
Abstract: We present observations of the J=1-0 line of CO and of the millimeter
recombination lines H30 , H35
, H35 , H38
, H38 and H39
and H39 toward the radio
star MWC349.
The profiles of the H35
toward the radio
star MWC349.
The profiles of the H35 and H39
and H39 lines show new narrow features (linewidths
of 15-20 kms
lines show new narrow features (linewidths
of 15-20 kms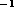 ) at radial velocities of -58 and 58 kms
) at radial velocities of -58 and 58 kms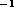 , close to the
terminal velocity of the ionized wind. These features are time variable and
their intensities for different quantum numbers (strong emission in the
H35
, close to the
terminal velocity of the ionized wind. These features are time variable and
their intensities for different quantum numbers (strong emission in the
H35 line and relatively weak in the H30
line and relatively weak in the H30 line) are inconsistent with LTE emission.
Therefore these new high--velocity features are very likely radio recombination
line masers (high--velocity masers). Contrary to the millimeter recombination
line masers previously discovered in this source at radial velocities of 30 and
-14 kms
line) are inconsistent with LTE emission.
Therefore these new high--velocity features are very likely radio recombination
line masers (high--velocity masers). Contrary to the millimeter recombination
line masers previously discovered in this source at radial velocities of 30 and
-14 kms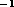 (low--velocity masers) whose intensity increases by a factor
(low--velocity masers) whose intensity increases by a factor
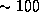 between the H39
between the H39 and the H30
and the H30 line, the high--velocity maser
intensity increases by only a factor of
line, the high--velocity maser
intensity increases by only a factor of 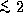 . We propose a two--component
model which qualitatively explains the radial velocities and the line intensity
characteristics of the two kind of masers observed in this source. In this
model, the high--velocity masers arise from the ionized stellar wind and the
low--velocity masers from the interface region of the ionized stellar wind and
the neutral disk around MWC349. The radial velocity separation of the
low--velocity maser spikes as a function quantum number deviates from that
expected for a disk in keplerian rotation.
. We propose a two--component
model which qualitatively explains the radial velocities and the line intensity
characteristics of the two kind of masers observed in this source. In this
model, the high--velocity masers arise from the ionized stellar wind and the
low--velocity masers from the interface region of the ionized stellar wind and
the neutral disk around MWC349. The radial velocity separation of the
low--velocity maser spikes as a function quantum number deviates from that
expected for a disk in keplerian rotation.
We have estimated the CO emission toward MWC349 by subtracting from the spectra
of the blended CO and H38 line that of the H39
line that of the H39 line. We detect a narrow
(
line. We detect a narrow
(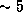 kms
kms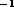 ) absorption line plus a broad (linewidth of
) absorption line plus a broad (linewidth of 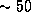 kms
kms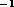 )
emission. The broad emission is only tentatively detected because of the
procedure used to derive it. We discuss the possible association of the CO
features with neutral circumstellar material in MWC349.
)
emission. The broad emission is only tentatively detected because of the
procedure used to derive it. We discuss the possible association of the CO
features with neutral circumstellar material in MWC349.



Next: Efficient mapping of
Up: Scientific Results
Previous: A Direct Image
Robert Lucas
Thu Mar 9 12:58:13 MET 1995
 line that of the H39
line that of the H39 line. We detect a narrow
(
line. We detect a narrow
(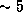 kms
kms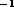 ) absorption line plus a broad (linewidth of
) absorption line plus a broad (linewidth of 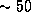 kms
kms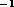 )
emission. The broad emission is only tentatively detected because of the
procedure used to derive it. We discuss the possible association of the CO
features with neutral circumstellar material in MWC349.
)
emission. The broad emission is only tentatively detected because of the
procedure used to derive it. We discuss the possible association of the CO
features with neutral circumstellar material in MWC349. 


 , R. Neri
, R. Neri ,
C. Thum
,
C. Thum , P. Planesas
, P. Planesas , R. Bachiller
, R. Bachiller
 Centro Astronómico de Yebes (IGN), Apartado 148, E-19080
Guadalajara, Spain
Centro Astronómico de Yebes (IGN), Apartado 148, E-19080
Guadalajara, Spain  IRAM, 300 rue de la Piscine, F-38406 St Martin d'Hères, France
IRAM, 300 rue de la Piscine, F-38406 St Martin d'Hères, France  , H35
, H35 , H38
, H38 and H39
and H39 toward the radio
star MWC349.
The profiles of the H35
toward the radio
star MWC349.
The profiles of the H35 and H39
and H39 lines show new narrow features (linewidths
of 15-20 kms
lines show new narrow features (linewidths
of 15-20 kms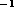 ) at radial velocities of -58 and 58 kms
) at radial velocities of -58 and 58 kms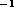 , close to the
terminal velocity of the ionized wind. These features are time variable and
their intensities for different quantum numbers (strong emission in the
H35
, close to the
terminal velocity of the ionized wind. These features are time variable and
their intensities for different quantum numbers (strong emission in the
H35 line and relatively weak in the H30
line and relatively weak in the H30 line) are inconsistent with LTE emission.
Therefore these new high--velocity features are very likely radio recombination
line masers (high--velocity masers). Contrary to the millimeter recombination
line masers previously discovered in this source at radial velocities of 30 and
-14 kms
line) are inconsistent with LTE emission.
Therefore these new high--velocity features are very likely radio recombination
line masers (high--velocity masers). Contrary to the millimeter recombination
line masers previously discovered in this source at radial velocities of 30 and
-14 kms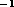 (low--velocity masers) whose intensity increases by a factor
(low--velocity masers) whose intensity increases by a factor
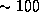 between the H39
between the H39 and the H30
and the H30 line, the high--velocity maser
intensity increases by only a factor of
line, the high--velocity maser
intensity increases by only a factor of 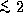 . We propose a two--component
model which qualitatively explains the radial velocities and the line intensity
characteristics of the two kind of masers observed in this source. In this
model, the high--velocity masers arise from the ionized stellar wind and the
low--velocity masers from the interface region of the ionized stellar wind and
the neutral disk around MWC349. The radial velocity separation of the
low--velocity maser spikes as a function quantum number deviates from that
expected for a disk in keplerian rotation.
. We propose a two--component
model which qualitatively explains the radial velocities and the line intensity
characteristics of the two kind of masers observed in this source. In this
model, the high--velocity masers arise from the ionized stellar wind and the
low--velocity masers from the interface region of the ionized stellar wind and
the neutral disk around MWC349. The radial velocity separation of the
low--velocity maser spikes as a function quantum number deviates from that
expected for a disk in keplerian rotation.