



Next: The molecular outflow and
Up: Scientific results
Previous: J=1-0 synthesis images
V. Bujarrabal  , J. Alcolea
, J. Alcolea  , R. Neri
, R. Neri  ,
M. Grewing
,
M. Grewing 
 Observatorio Astronómico Nacional (I.G.N), Apartado 1143,
E-28800 Alcalá de Henares, Spain
Observatorio Astronómico Nacional (I.G.N), Apartado 1143,
E-28800 Alcalá de Henares, Spain
 Institut de Radio Astronomie Millimétrique (IRAM), 300 Rue
de la Piscine, F-38406 Saint Martin d'Hères, France
Institut de Radio Astronomie Millimétrique (IRAM), 300 Rue
de la Piscine, F-38406 Saint Martin d'Hères, France
Abstract: We present high-resolution 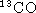 J=1-0 maps of the
protoplanetary nebula M1-92, Minkowski's Footprint, obtained with the
IRAM interferometer at Plateau de Bure. Previous
J=1-0 maps of the
protoplanetary nebula M1-92, Minkowski's Footprint, obtained with the
IRAM interferometer at Plateau de Bure. Previous 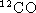 J=1-0
maps and single-dish observations of the J=1-0, J=2-1 and J=3-2
transitions in both isotopic substitutions are also discussed.
The cartography confirms the axial symmetry and complex structure
already found from
J=1-0
maps and single-dish observations of the J=1-0, J=2-1 and J=3-2
transitions in both isotopic substitutions are also discussed.
The cartography confirms the axial symmetry and complex structure
already found from 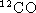 data. The gas velocity presents a
dominant axial component that increases in absolute value from the
center, up to a (de-projected) velocity of 70 kms
data. The gas velocity presents a
dominant axial component that increases in absolute value from the
center, up to a (de-projected) velocity of 70 kms 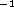 . Most of the
observed emission is at velocities clearly above the expected AGB
expansion kinematics. This fact, together with a remarkable continuity
found along the axis in the structure and velocity of the nebula, is
interpreted as showing that the present CO nebula has been shaped by
momentum transport from the fast post-AGB flow to the rest of the
(AGB) envelope, probably by means of a bow-like shock.
. Most of the
observed emission is at velocities clearly above the expected AGB
expansion kinematics. This fact, together with a remarkable continuity
found along the axis in the structure and velocity of the nebula, is
interpreted as showing that the present CO nebula has been shaped by
momentum transport from the fast post-AGB flow to the rest of the
(AGB) envelope, probably by means of a bow-like shock.
The comparison of the different transitions is used to deduce the
physical conditions in the molecular gas. Most of the observed
(post-shock) material is found to have a low temperature of about
15K, indicating that the cooling processes are efficient after the
passage of the shock. Typical densities of
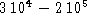 cm
cm 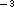 are deduced, corresponding to a total gas
mass of about 1 M
are deduced, corresponding to a total gas
mass of about 1 M 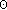 . This high value shows that most of the
nebular material is molecular and probed by the CO
observations. Therefore, our maps effectively represent the disruption
of the AGB envelope by the passage of a shock, allowing a description
of the physical conditions in the nebula during this evolutionary
phase.
. This high value shows that most of the
nebular material is molecular and probed by the CO
observations. Therefore, our maps effectively represent the disruption
of the AGB envelope by the passage of a shock, allowing a description
of the physical conditions in the nebula during this evolutionary
phase.




Next: The molecular outflow and
Up: Scientific results
Previous: J=1-0 synthesis images
lucas@iram.fr
![]() cm
cm ![]() are deduced, corresponding to a total gas
mass of about 1 M
are deduced, corresponding to a total gas
mass of about 1 M ![]() . This high value shows that most of the
nebular material is molecular and probed by the CO
observations. Therefore, our maps effectively represent the disruption
of the AGB envelope by the passage of a shock, allowing a description
of the physical conditions in the nebula during this evolutionary
phase.
. This high value shows that most of the
nebular material is molecular and probed by the CO
observations. Therefore, our maps effectively represent the disruption
of the AGB envelope by the passage of a shock, allowing a description
of the physical conditions in the nebula during this evolutionary
phase.