



Next: The pointing of
Up: Scientific Results
Previous: Scientific Results
F. Gueth , S. Guilloteau
, S. Guilloteau , R. Bachiller
, R. Bachiller
 Institut de Radio Astronomie Millimétrique,
300 rue de la Piscine, F-38406 Saint Martin d'Hères, France
Institut de Radio Astronomie Millimétrique,
300 rue de la Piscine, F-38406 Saint Martin d'Hères, France
 Centro Astronómico de Yebes, Apartado 148, E-19080 Guadalajara,
Spain
Centro Astronómico de Yebes, Apartado 148, E-19080 Guadalajara,
Spain
Abstract: The blue-shifted lobe of the L 1157 molecular outflow has been
imaged in the CO J=1-0 line, and in the 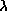 2.6 mm
continuum, with angular resolution of
2.6 mm
continuum, with angular resolution of 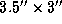 (
(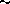 7
7
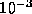 pc at the distance of L 1157, 440 pc) at the IRAM
interferometer. The data consist of a mosaic of 10 partially
overlapping fields, complemented with short spacing information from
the IRAM 30-m telescope.
pc at the distance of L 1157, 440 pc) at the IRAM
interferometer. The data consist of a mosaic of 10 partially
overlapping fields, complemented with short spacing information from
the IRAM 30-m telescope.
The images reveal the presence of at least two prominent
limb brightened cavities which have been likely created by the
propagation of large bow shocks due to episodic events in a
precessing, highly collimated jet. A simple spatio-kinematic model
involving two different ejection events provides an accurate
description of the observations. We find that the outflow is inclined
by 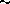 80 to the line of sight, and that the axis of the
underlying jet precesses on a cone of 6 opening angle, with a
period of
80 to the line of sight, and that the axis of the
underlying jet precesses on a cone of 6 opening angle, with a
period of 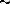 4000 yr. We discuss the constraints derived from the
present observations on several recent models for jet driven
molecular outflows. We conclude that, similarly to what happens in
other outflows (e.g.: L1448), the large opening angle of the
L 1157 CO outflow is originated by the large size of the
propagating bow shocks, since the precession in L 1157 happens in
a narrow cone. However, the observed shape of the cavities evacuated
by the bow shock propagation are not well accounted for by current
models of gas entrainment by bow shocks.
4000 yr. We discuss the constraints derived from the
present observations on several recent models for jet driven
molecular outflows. We conclude that, similarly to what happens in
other outflows (e.g.: L1448), the large opening angle of the
L 1157 CO outflow is originated by the large size of the
propagating bow shocks, since the precession in L 1157 happens in
a narrow cone. However, the observed shape of the cavities evacuated
by the bow shock propagation are not well accounted for by current
models of gas entrainment by bow shocks.
Robert Lucas
Mon Sep 18 09:50:01 METDST 1995
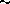 80 to the line of sight, and that the axis of the
underlying jet precesses on a cone of 6 opening angle, with a
period of
80 to the line of sight, and that the axis of the
underlying jet precesses on a cone of 6 opening angle, with a
period of 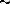 4000 yr. We discuss the constraints derived from the
present observations on several recent models for jet driven
molecular outflows. We conclude that, similarly to what happens in
other outflows (e.g.: L1448), the large opening angle of the
L 1157 CO outflow is originated by the large size of the
propagating bow shocks, since the precession in L 1157 happens in
a narrow cone. However, the observed shape of the cavities evacuated
by the bow shock propagation are not well accounted for by current
models of gas entrainment by bow shocks.
4000 yr. We discuss the constraints derived from the
present observations on several recent models for jet driven
molecular outflows. We conclude that, similarly to what happens in
other outflows (e.g.: L1448), the large opening angle of the
L 1157 CO outflow is originated by the large size of the
propagating bow shocks, since the precession in L 1157 happens in
a narrow cone. However, the observed shape of the cavities evacuated
by the bow shock propagation are not well accounted for by current
models of gas entrainment by bow shocks.



 , S. Guilloteau
, S. Guilloteau , R. Bachiller
, R. Bachiller
 Institut de Radio Astronomie Millimétrique,
300 rue de la Piscine, F-38406 Saint Martin d'Hères, France
Institut de Radio Astronomie Millimétrique,
300 rue de la Piscine, F-38406 Saint Martin d'Hères, France Centro Astronómico de Yebes, Apartado 148, E-19080 Guadalajara,
Spain
Centro Astronómico de Yebes, Apartado 148, E-19080 Guadalajara,
Spain 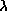 2.6 mm
continuum, with angular resolution of
2.6 mm
continuum, with angular resolution of 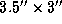 (
(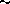 7
7
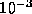 pc at the distance of L 1157, 440 pc) at the IRAM
interferometer. The data consist of a mosaic of 10 partially
overlapping fields, complemented with short spacing information from
the IRAM 30-m telescope.
pc at the distance of L 1157, 440 pc) at the IRAM
interferometer. The data consist of a mosaic of 10 partially
overlapping fields, complemented with short spacing information from
the IRAM 30-m telescope.