


Next: 7.3.1 Phase referencing by
Up: 7. Band pass and
Previous: 7.2.4 Side band calibration
We now turn to the more difficult problem of correcting for the time dependence of the
complex gains, contained in the functions
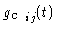 . Variations occur in both amplitude
and phase. Let us summarize the various effects to be calibrated:
. Variations occur in both amplitude
and phase. Let us summarize the various effects to be calibrated:
- Interferometer geometry:
Small errors in the baseline determination will cause slow phase
drifts (period 24 hours); unfortunately these errors are dependent
on the source direction so they cannot be properly calibrated out by
phase referencing on a calibrator, only reduced by a factor of the
order of the source to calibrator distance expressed in radians.
- Atmosphere
The atmosphere introduces phase fluctuations on time scales 1s
to a few hours, depending on baseline length and atmospheric
conditions (see previous lecture). The effect of fluctuations on
short time scales is to cause loss of amplitude by decorrelation,
while on the long term the phase fluctuations can be mistaken for
structure in the source itself. The critical time there is the time
it takes for the projected baseline vector to move by half the
diameter of one antenna:
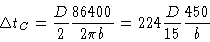 |
(7.21) |
This time ranges from 4 minutes to 1 hour for Plateau de Bure,
depending on the baseline length.
The phase fluctuations on short time scales may be corrected by applying the
radiometric phase correction method, if it is available.
- Antennas
The antennas may cause variations in amplitude gains due to
degradation in the pointing and in the focusing due to thermal
deformations in the antennas. These can be corrected to first order
by amplitude calibration but it is much better to keep the errors
low by proper frequent monitoring of the pointing and focus, since
these errors affect differently sources at the center and at the
edges of the field. Focus errors also cause strong phase errors due
to the additional path length which is twice the sub reflector motion
in the axial direction.
- Electronics
Phase and amplitude drifts in the electronics are kept low by
efficient design (see the lectures on receivers and signal and LO
transport). The electronics phase drifts are generally slow and of
low amplitude, expect for hardware problems.
A detailed analysis can be found in [Lay 1997].



Next: 7.3.1 Phase referencing by
Up: 7. Band pass and
Previous: 7.2.4 Side band calibration
S.Guilloteau
2000-01-19
![]() . Variations occur in both amplitude
and phase. Let us summarize the various effects to be calibrated:
. Variations occur in both amplitude
and phase. Let us summarize the various effects to be calibrated: