

Up: IRAM Newsletter 55 (February 2003)
Previous: Ongoing modernization of GILDAS
Subsections
C. Codella(1), R. Bachiller(2), M. Benedettini(3)
and P. Caselli(4)
(1)Istituto di Radioastronomia, CNR, Sezione di Firenze, Largo E. Fermi
5, 50125 Firenze, Italy,
(2)Observatorio Astronómico Nacional (IGN), Apartado 1143,
E-28800, Alcalá de Henares (Madrid), Spain,
(3)Istituto di Fisica dello Spazio Interplanetario, CNR,
Area di Ricerca Tor Vergata, Via Fosso del Cavaliere 100, 00133 Roma, Italy,
(4)INAF, Osservatorio Astrofisico di Arcetri, Largo E. Fermi 5,
50125 Firenze, Italy
Abstract:
The Cepheus A star forming region has been investigated through a
multiline H2S and SO2 survey at mm-wavelengths. Large scale
maps and high-resolution line profiles reveal the occurrence of
several outflows. CepA-East is associated with multiple mass loss
processes: in particular, we detect a 0.6 pc jet-like
structure which shows for the first time that the CepA-East YSOs are driving
a collimated outflow moving towards the south.
The observed outflows show different clumps associated with definitely
different H2S/SO2 integrated emission
ratios indicating that the gas chemistry in Cepheus A
has been altered by the passage of shocks.
H2S appears to be more abundant than SO2 in high velocity clumps, in
agreement with chemical models.
However, we also find quite narrow H2S linewidths, suggesting of regions
where the evaporated H2S molecules had enough time to slow down but
not to freeze out onto dust grains.
Finally, the comparison between the
line profiles indicates that the excitation conditions increase with the
velocity, as expected for a propagation of collimated bow shocks.
MNRAS, in press
C. De Breuck(1), R. Neri(2) and A. Omont(1)
(1)Institute d'Astrophysique de Paris, 98bis Boulevard Arago,
75014 Paris, France,
(2)Institute de Radio Astronomie Millimétrique,
38406 St. Martin d'Hères, France
Abstract:
We report on the detection of the CO(4-3) line with the IRAM Plateau de
Bure Interferometer in two z>3 radio galaxies, doubling the number of
successful detections in such objects. A comparison of the CO and
Ly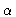 velocity profiles indicates that in at least half of the cases,
the CO is coincident in velocity with associated HI absorption seen
against the Ly
velocity profiles indicates that in at least half of the cases,
the CO is coincident in velocity with associated HI absorption seen
against the Ly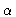 emission. This strongly suggests that the CO and HI
originate from the same gas reservoir, and could explain the observed
redshift differences between the optical narrow emission lines and the CO.
The CO emission traces a mass of H2 100-1000 times larger than the HI
and HII mass traced by Ly
emission. This strongly suggests that the CO and HI
originate from the same gas reservoir, and could explain the observed
redshift differences between the optical narrow emission lines and the CO.
The CO emission traces a mass of H2 100-1000 times larger than the HI
and HII mass traced by Ly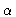 ,
providing sufficient gas to supply the
massive starbursts suggested by their strong thermal dust emission.
,
providing sufficient gas to supply the
massive starbursts suggested by their strong thermal dust emission.
To appear in: Proceedings of the conference "Radio Galaxies: Past,
present and future", Leiden, 11-15 Nov. 2002, eds. M. Jarvis et al.,
Elsevier Science


Up: IRAM Newsletter 55 (February 2003)
Previous: Ongoing modernization of GILDAS
bremer@iram.fr