


Next: New Preprints
Up: Scientific Results
Previous: The distorted kinematics
J. Crovisier , N. Biver
, N. Biver , D. Bockelée-Morvan
, D. Bockelée-Morvan , P.
Colom
, P.
Colom , L. Jorda
, L. Jorda , E. Lellouch
, E. Lellouch , G. Paubert
, G. Paubert , and D.
Despois
, and D.
Despois
 Observatoire de Paris-Meudon, F-9219 Meudon, France
Observatoire de Paris-Meudon, F-9219 Meudon, France
 IRAM, Avenida Divina Pastora, 7, E-18012 Granada, Spain
IRAM, Avenida Divina Pastora, 7, E-18012 Granada, Spain
 Observatoire de Bordeaux, BP 89, F-33270 Floirac, France
Observatoire de Bordeaux, BP 89, F-33270 Floirac, France
Abstract: P/Schwassmann-Wachmann 1 is a peculiar comet on a nearly
circular orbit at 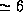 AU from the Sun. It undergoes strong,
unpredictable outbursts which cannot be explained by water sublimation at this
large heliocentric distance. The recent detection of the
AU from the Sun. It undergoes strong,
unpredictable outbursts which cannot be explained by water sublimation at this
large heliocentric distance. The recent detection of the 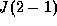 line of CO
at the JCMT (Senay & Jewitt 1994, Nature 371, 229) suggested that
carbon monoxide may be responsible for this activity.
line of CO
at the JCMT (Senay & Jewitt 1994, Nature 371, 229) suggested that
carbon monoxide may be responsible for this activity.
We observed the 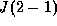 and
and 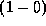 lines of CO in comet
P/Schwassmann-Wachmann 1 at IRAM 30-m with high spectral resolution at four
different epochs. The line profile is dominated by a very narrow (0.14 km
sec
lines of CO in comet
P/Schwassmann-Wachmann 1 at IRAM 30-m with high spectral resolution at four
different epochs. The line profile is dominated by a very narrow (0.14 km
sec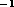 FWHM) component blueshifted by 0.48 km sec
FWHM) component blueshifted by 0.48 km sec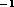 , with a fainter
component redshifted at 0.30 km sec
, with a fainter
component redshifted at 0.30 km sec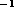 (Fig. 7).
We infer that CO is preferentially
outgassed from the day side of the nucleus, percolating through a porous mantle
of ice or dust rather than sublimating from pure exposed ice. From the line
width of the narrow component and from the line intensity ratio of the two
lines we estimate cold (
(Fig. 7).
We infer that CO is preferentially
outgassed from the day side of the nucleus, percolating through a porous mantle
of ice or dust rather than sublimating from pure exposed ice. From the line
width of the narrow component and from the line intensity ratio of the two
lines we estimate cold (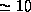 K) kinetic and rotational temperatures. The
CO production rate,
K) kinetic and rotational temperatures. The
CO production rate, 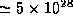 sec
sec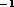 in this distant comet
and comparable to that of P/Halley near the Sun, is high enough to explain the
release of dust and its activity observed in the visible.
in this distant comet
and comparable to that of P/Halley near the Sun, is high enough to explain the
release of dust and its activity observed in the visible.
(To be published in ICARUS)
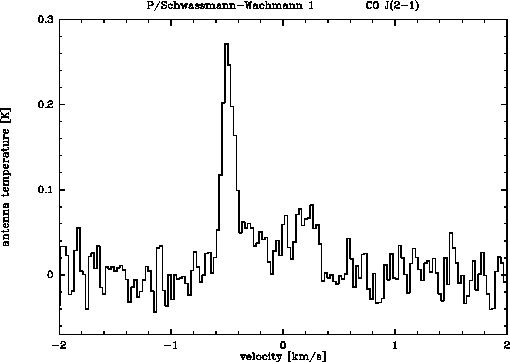
Figure: The CO 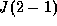 observed at the IRAM 30-m telescope in comet
P/Schwassmann-Wachmann 1 (average of Sept. 3-4 and Oct. 4-5 1994). The
velocity scale is with respect to the comet frame of rest.
observed at the IRAM 30-m telescope in comet
P/Schwassmann-Wachmann 1 (average of Sept. 3-4 and Oct. 4-5 1994). The
velocity scale is with respect to the comet frame of rest.



Next: New Preprints
Up: Scientific Results
Previous: The distorted kinematics
Robert Lucas
Thu Mar 9 12:14:01 MET 1995
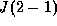 and
and 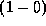 lines of CO in comet
P/Schwassmann-Wachmann 1 at IRAM 30-m with high spectral resolution at four
different epochs. The line profile is dominated by a very narrow (0.14 km
sec
lines of CO in comet
P/Schwassmann-Wachmann 1 at IRAM 30-m with high spectral resolution at four
different epochs. The line profile is dominated by a very narrow (0.14 km
sec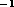 FWHM) component blueshifted by 0.48 km sec
FWHM) component blueshifted by 0.48 km sec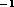 , with a fainter
component redshifted at 0.30 km sec
, with a fainter
component redshifted at 0.30 km sec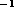 (Fig. 7).
We infer that CO is preferentially
outgassed from the day side of the nucleus, percolating through a porous mantle
of ice or dust rather than sublimating from pure exposed ice. From the line
width of the narrow component and from the line intensity ratio of the two
lines we estimate cold (
(Fig. 7).
We infer that CO is preferentially
outgassed from the day side of the nucleus, percolating through a porous mantle
of ice or dust rather than sublimating from pure exposed ice. From the line
width of the narrow component and from the line intensity ratio of the two
lines we estimate cold (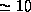 K) kinetic and rotational temperatures. The
CO production rate,
K) kinetic and rotational temperatures. The
CO production rate, 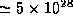 sec
sec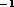 in this distant comet
and comparable to that of P/Halley near the Sun, is high enough to explain the
release of dust and its activity observed in the visible.
in this distant comet
and comparable to that of P/Halley near the Sun, is high enough to explain the
release of dust and its activity observed in the visible. 


 , N. Biver
, N. Biver , D. Bockelée-Morvan
, D. Bockelée-Morvan , P.
Colom
, P.
Colom , L. Jorda
, L. Jorda , E. Lellouch
, E. Lellouch , G. Paubert
, G. Paubert , and D.
Despois
, and D.
Despois
 Observatoire de Paris-Meudon, F-9219 Meudon, France
Observatoire de Paris-Meudon, F-9219 Meudon, France IRAM, Avenida Divina Pastora, 7, E-18012 Granada, Spain
IRAM, Avenida Divina Pastora, 7, E-18012 Granada, Spain Observatoire de Bordeaux, BP 89, F-33270 Floirac, France
Observatoire de Bordeaux, BP 89, F-33270 Floirac, France 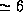 AU from the Sun. It undergoes strong,
unpredictable outbursts which cannot be explained by water sublimation at this
large heliocentric distance. The recent detection of the
AU from the Sun. It undergoes strong,
unpredictable outbursts which cannot be explained by water sublimation at this
large heliocentric distance. The recent detection of the 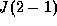 line of CO
at the JCMT (Senay & Jewitt 1994, Nature 371, 229) suggested that
carbon monoxide may be responsible for this activity.
line of CO
at the JCMT (Senay & Jewitt 1994, Nature 371, 229) suggested that
carbon monoxide may be responsible for this activity.

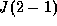 observed at the IRAM 30-m telescope in comet
P/Schwassmann-Wachmann 1 (average of Sept. 3-4 and Oct. 4-5 1994). The
velocity scale is with respect to the comet frame of rest.
observed at the IRAM 30-m telescope in comet
P/Schwassmann-Wachmann 1 (average of Sept. 3-4 and Oct. 4-5 1994). The
velocity scale is with respect to the comet frame of rest.