


Next: 13.7 Deconvolution
Up: 13. The Imaging Principles
Previous: 13.5 Weighing and Tapering
We have now introduced the basic parameters of the imaging process: gridding, weighting
and tapering. The main imaging task in the GILDAS software is UV_MAP. Before
using UV_MAP, it is also recommended to use the associated
task UV_STAT which evaluates the beam sizes, point source and brightness
sensitivity as function of taper or robust weighting parameter.
Although the choice of configurations for the Plateau de Bure interferometer has been performed in order to
optimize the uv coverage for most observing conditions, robust weighting can often
offer a better compromise, unless signal to noise is insufficient. Task UV_STAT also suggests appropriate pixel sizes for UV_MAP
The imaging task UV_MAP is controlled by the following parameters:
- MAP_SIZE
The number of pixels in each direction. This should be powers of 2.
- MAP_CELL
The pixel size, in arcsecond, in each direction. It should respect proper sampling
compared to the synthesized beam width. In practice, 3 - 4 pixels per beam width
are required. Task UV_STAT can compute the optimum value for this parameter.
Note that the imaged area is MAP_SIZE 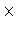 MAP_CELL
MAP_CELL
- MCOL
For spectral line data, the first and last channel to be imaged. (0,0) means
all data.
- WCOL
The channel from which the natural weights S are taken. UV_MAP
produces only one beam for all channels (by default, there is an alternate
option for experts). WCOL = 0 is equivalent to
WCOL = (MCOL[1]+MCOL[2])/2.
- WEIGHT_MODE
UN for Uniform or NA for Natural weighting.
UNiform weighting is actually a Robust weighting in
UV_MAP.
- UV_CELL
When UNiform weighting is used, UV_CELL[1] is the UV cell diameter
(in meters), and UV_CELL[2] is the threshold for robust weighting:
1 corresponds to the mean natural weight of all cells. UV_CELL[1]
should normally be 7.5 m for Plateau de Bure data.
- CONVOLUTION
This is the convolution type for gridding. Choices are offered for test purposes,
but CONVOLUTION = 5 (Spheroidal) gives best results.
The other parameters are used to re-center the map (by phase shifting the uv data
before imaging) when needed. This is convenient for Mosaics. UV_MAP
performs all the imaging steps presented before: gridding, weighting, tapering,
correction for gridding function, and computes the dirty beam and dirty image.
Both UV_STAT and UV_MAP are implemented as commands in the
MAPPING program, or as tasks available from the GRAPHIC program. Using one
or the other is a matter of personal preference.



Next: 13.7 Deconvolution
Up: 13. The Imaging Principles
Previous: 13.5 Weighing and Tapering
S.Guilloteau
2000-01-19