


Next: 5.1.2 The heterodyne interferometer
Up: 5.1 An Heterodyne Interferometer
Previous: 5.1 An Heterodyne Interferometer
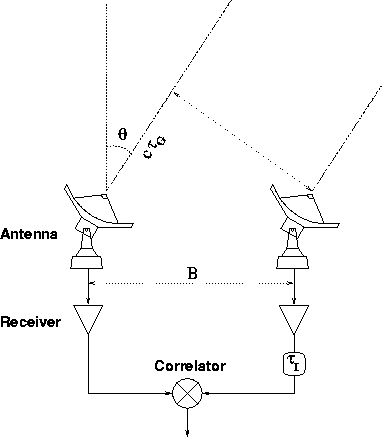
This is composed of 2 antennas, a multiplier, an integrator
(Fig. 5.1); we directly multiply the signals, and
average in time.
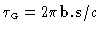 is the geometrical
delay.
is the geometrical
delay.
Figure 5.1:
A simple, two-antenna
interferometer
 |
Provided the geometrical delay is compensated in the hardware, after
filtering out the high frequency terms, the output of the correlator
is the real part of the visibility:
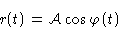 |
(5.1) |
A complex correlator using a quadrature network can be used to mesure
the imaginary part; or (equivalently) one uses a spectral
correlator.
S.Guilloteau
2000-01-19
