Next: 3.3 Available Resolution
Up: 3. Millimetre Very Long
Previous: 3.1 Introduction
Contents
Subsections
The wet atmosphere, even at high altitudes, has transmission windows at
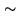 3mm (
3mm (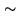 100GHz),
100GHz), 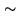 2mm
(
2mm
(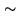 150GHz),
150GHz), 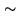 1.3mm (
1.3mm (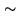 230GHz), and at
shorter wavelengths, through which radio signals can propagate to
the surface of the Earth. The observing facilities of mm-VLBI,
summarized in Table 3.1, make use of these atmospheric
windows. cm The remark 'Proposal' in
Table 3.1 indicates that the array is available to
observers on a competitive proposal basis. The 2-mm and 1.3-mm
observations are in an experimental state. The mentioned 1.3-mm
observations were experimental, and successful.
230GHz), and at
shorter wavelengths, through which radio signals can propagate to
the surface of the Earth. The observing facilities of mm-VLBI,
summarized in Table 3.1, make use of these atmospheric
windows. cm The remark 'Proposal' in
Table 3.1 indicates that the array is available to
observers on a competitive proposal basis. The 2-mm and 1.3-mm
observations are in an experimental state. The mentioned 1.3-mm
observations were experimental, and successful.
Table 3.1:
mm-VLBI Arrays and Experimental Observations
| Frequency(Wavel.) |
Array |
Telescopes |
Baseline |
Observing |
| 86GHz (3.5mm) |
CMVA |
Table 2 |
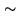 8000km 8000km |
Proposal |
| 86GHz (3.5mm) |
VLBA(*) |
Table 3 |
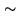 8000km 8000km |
Proposal |
| 150GHz (2.0mm) |
-- |
PV-KP-SEST |
|
experim. |
| 230GHz (1.3mm) |
- |
OVRO-KP |
 500km 500km |
experim. (**) |
| |
- |
PV-PdBure |
 1000km 1000km |
experim. (***) |
PV: Pico Veleta (Spain), KP: Kitt Peak (USA), OVRO: Owens Valley
Obs. (USA), SEST: La Silla (Chile).
(*) sub-array of the VLBA
array (Table
3.3); (**) [
Padin et al. 1990]; (***)
[
Greve et al. 1995], [
Krichbaum et al. 1998]
Figure 3.1:
Observatories participating in cm and mm-wavelength
VLBI. The mm-VLBI observatories of the CMVA (Table 3.2)
are concentrated in Western Europe and North America. From
[Felli & Spencer 1989], Schilizzi p404, with kind permission from Kluwer
Academic Publishers.
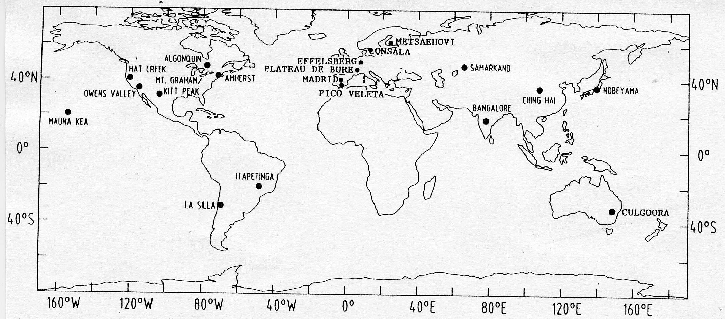 |

The CMVA (Coordinated Millimeter VLBI-)array contains the
telescopes of 12 observatories which operate together in
coordinated observations for approximately 15 days per year. The
telescopes are located in North-America, Europe, and Chile. The
performances of the telescopes at 86GHz (3.5mm) are given in
Table 3.2, the location of the telescopes is shown in
Figure 3.1. The European telescopes of the CMVA are
located essentially in the direction North-South, the American
telescopes are located essentially in the direction East-West. As
applied in other interferometers, the CMVA array uses Earth
rotation to obtain uv-coverage. Some of the strong mm-VLBI
sources (3C273, 3C279), which are regularly monitored (see
Figure 3.9), are located at low declination (Dec =
2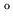 , -5
, -5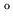 ) so that they can be simultaneously
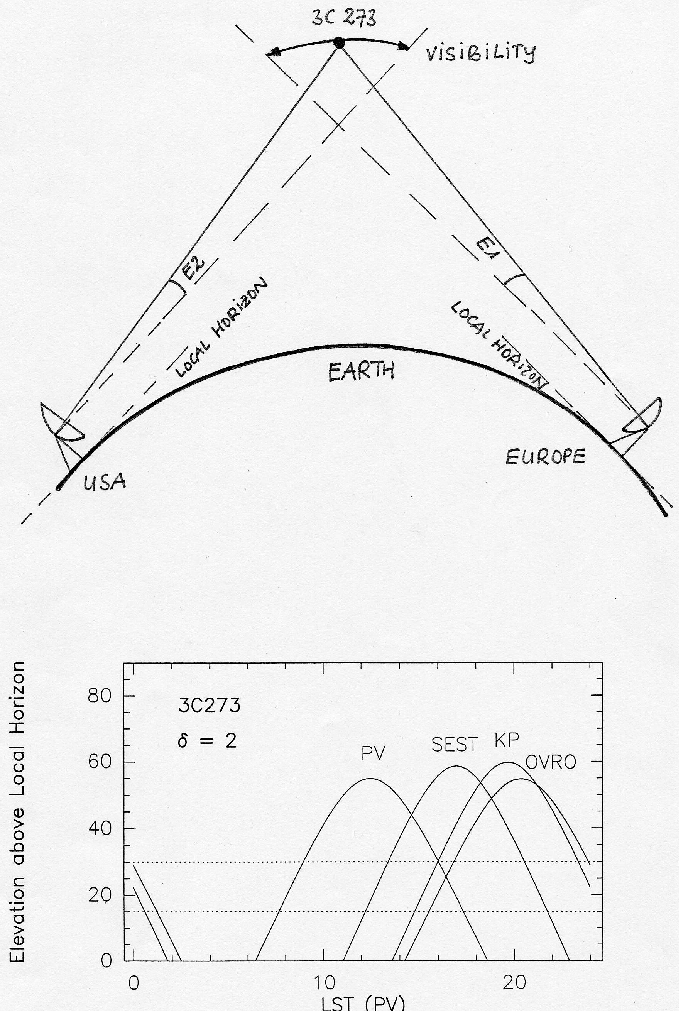
observed only at low local elevations, as illustrated in Figure
3.2 for 3C273 and the stations Pico Veleta - SEST -
Kitt Peak - Owens Valley. The low elevation usually implies a
high line-of-sight system temperature (T
) so that they can be simultaneously
observed only at low local elevations, as illustrated in Figure
3.2 for 3C273 and the stations Pico Veleta - SEST -
Kitt Peak - Owens Valley. The low elevation usually implies a
high line-of-sight system temperature (T
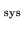 ), thus a
low signal-to-noise ratio, and thus a low detection sensitivity
(Sect.3.5). The low elevation implies also that the
uv-coverage may be incomplete, the synthesized beam asymmetric,
and the final map distorted. cm
contains also several telescopes
expected to be available in future. These are telescopes with
large collecting areas; the dedicated mm-wavelength telescopes
(PdB, LMT, ALMA) are located at high altitudes.
), thus a
low signal-to-noise ratio, and thus a low detection sensitivity
(Sect.3.5). The low elevation implies also that the
uv-coverage may be incomplete, the synthesized beam asymmetric,
and the final map distorted. cm
contains also several telescopes
expected to be available in future. These are telescopes with
large collecting areas; the dedicated mm-wavelength telescopes
(PdB, LMT, ALMA) are located at high altitudes.
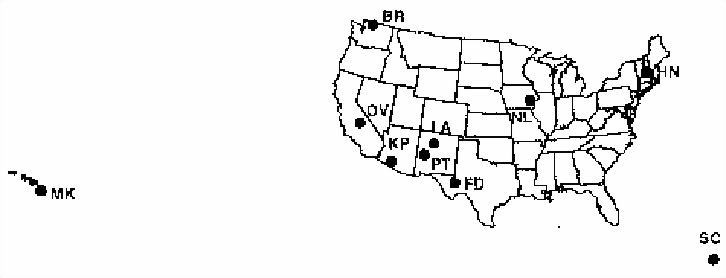
The VLBA (Very Long Baseline-)array, which consists of 10
dedicated 25-m diameter telescopes (Table 3.3,
Figure 3.3), is located on the North-American continent,
including one antenna on Hawaii. This array observes routinely at
43GHz. The array is being upgraded for observations at 86GHz
(3.5mm); a sub-array (+) is available for 86GHz VLBI
observations. Some of these telescopes collaborate in CMVA
observations.
Table:
The VLBA Array [10 25m antennas] (partially
operating at 86GHz)
25m antennas] (partially
operating at 86GHz)
| |
Code |
Location (USA) |
Elevation (m) |
| |
SC |
St. Croix VI |
16 |
| |
HN |
Hancock NH |
309 |
| + |
NL |
N. Liberty IA |
241 |
| + |
FD |
Ford Davis TX |
1616 |
| + |
LA |
Los Alamos NM |
1967 |
| + |
PT |
Pie Town NM |
2371 |
| + |
KP |
Kitt Peak AZ |
1916 |
| + |
OV |
Owens Valley CA |
1207 |
| |
BR |
Brewster WA |
255 |
| + |
MK |
Mauna Kea HI |
3720 |




Next: 3.3 Available Resolution
Up: 3. Millimetre Very Long
Previous: 3.1 Introduction
Contents
Anne Dutrey